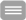GABA is the most important inhibitory neurotransmitter in the adult brain. But during early development, GABA acts mostly depolarizing/excitatory (see figure). Considering the hypothesis of an activity-dependent optimization of neuronal circuits we want to determine the biological relevance of GABA-mediated excitation during development for the maturation of neuronal circuits in the brain.
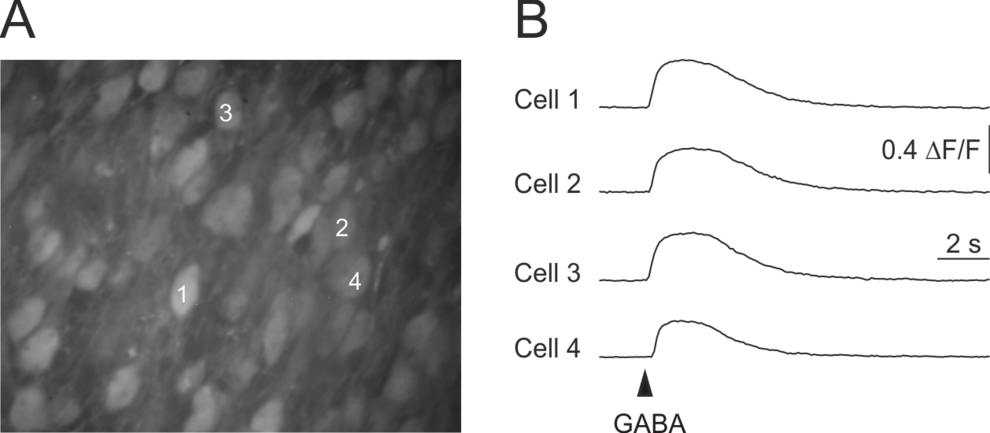
GABA-induced somatic [Ca2+]-transients in an acute brain slice of a 3 day old mouse. A, Confocal fluorescence image of a part of the upper cortical plate in the occipital cortex, stained with the high affinity Ca2+-indicator dye Oregon Green 488 BAPTA-1 (AM). B, Application of GABA (100 µM, 200 ms) induced a transient increase in intracellular (somatic) Ca2+-concentration. Latter is caused by the activation of voltage-gated Ca2+-channels and therefore an indication of GABAergic depolarization.
References:
- Weiler S, Teichert M, Margrie TW (2024) Layer 6 coricocortical cells dominate the anatomical organization of intra and interhemispheric feedback, eLife. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.100478.1
- Graf J, Samiree A, Flossmann T, Holthoff K, Kirmse K (2024) Chemogenetic silencing reveals presynaptic Gi/o protein mediated inhibition of synchronized activity in the developing hippocampus in vivo. iScience. DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.110997
- Teichert M, Gull S, Herrmann KH, Gaser C, Reichenbach JR, Urbach A, Frahm C, Holthoff K, Witte OW, Schmidt S (2024) Harnessing early multimodal motor training to drive motor recovery and brain-wide structural reorganization after stroke. bioRxiv doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.07.03.601837
- Graf J, Samiree A, Flossmann T, Holthoff K, Kirmse K (2024) Chemogenetic silencing reveals presynaptic Gi/o protein mediated inhibition of synchronized activity in the developing hippocampus in vivo. bioRxiv doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.02.02.578550
- Weiler S, Teichert M, Margrie TW (2024) Layer 6 corticocortical cells dominate the anatomical organization of intra and interhemispheric feedback. bioRxiv doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.05.01.590702oRxiv
- Weiler S, Rahmati V, Isstas M, Wutke J, Stark AW, Franke C, Graf J, Geis C, Witte OW, Hübener M, Bolz J, Margrie TW, Holthoff K, Teichert M (2024) A primary sensory cortical interareal feedforward inhibitory circuit for tacto-visual integration. Nat Commun 15, 3081. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-47459-2
- Graf J, Rahmati V, Majoros M, Witte OW, Geis C, Kiebel SJ, Holthoff K, Kirmse K (2022) Network instability dynamics drive a transient bursting period in the developing hippocampus in vivo. eLife 11:e82756. DOI: https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.82756
- Weiler S, Rahmati V, Isstas M, Wutke J, Stark AW, Franke C, Geis C, Witte OW, Huebener M, Bolz J, Margrie TW, Holthoff K, Teichert M (2022) A primary sensory cortical interareal feedforward inhibitory circuit for tacto-visual integration. bioRxiv 2022.11.04.515161; doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.11.04.515161
- Graf J, Rahmati V, Majoros M, Witte OW, Geis C, Kiebel SJ, Holthoff K, Kirmse K (2022) Network instability dynamics drive a transient bursting period in the developing hippocampus in vivo. bioRxiv doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.05.28.446133
- Graf J, Zhang C, Marguet SL, Herrmann T, Flossmann T, Hinsch R, Rahmati V, Guenther M, Frahm C, Urbach A, Neves RM, Witte OW, Kiebel SJ, Isbrandt D, Hübner CA, Holthoff K, Kirmse K (2021) A limited role of NKCC1 in telencephalic glutamatergic neurons for developing hippocampal network dynamics and behavior. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Apr 6;118(14):e2014784118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2014784118
- Graf J, Zhang C, Marguet SL, Herrmann T, Flossmann T, Hinsch R, Rahmati V, Guenther M, Frahm C, Urbach A, Neves RM, Witte OW, Kiebel SJ, Isbrandt D, Hübner CA, Holthoff K, Kirmse K (2020) Intraneuronal chloride accumulation via NKCC1 is not essential for hippocampal network development in vivo. doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.07.13.200014
- Kirmse K, Holthoff K (2020) Chloride transporter activities shape early brain circuit development, Book chapter in ´Neuronal Chloride Transporters in Health and Disease´, Academic Press, ISBN: 9780128153185
- Holthoff K (2020) The Janus-face of GABAergic synaptic transmission during brain development. J Physiol. doi: 10.1113/JP279623
- Zhang C, Yang S, Flossmann T, Gao S, Witte OW, Nagel G, Holthoff K, Kirmse K (2019) Optimized photo-stimulation of halorhodopsin for long-term neuronal inhibition. BMC Biology 17:95
- Kirmse K (2019) Editorial: GABAergic networks in the developing and mature brain. Brain Res. 1718:10-11. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2019.04.029
- Flossmann T, Kaas T, Rahmati V, Kiebel SJ, Witte OW, Holthoff K, Kirmse K (2019) Somatostatin Interneurons Promote Neuronal Synchrony in the Neonatal Hippocampus, Cell Rep 26(12):3173-3182.e5, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2019.02.061
- Prüss H, Kirmse K (2018) Pathogenetic role of autoantibodies against inhibitory synapses. Brain Res 1701:146-152. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2018.09.009.
- Rahmati V, Kirmse K, Holthoff K, Kiebel SJ (2018) Ultra-Fast Accurate Reconstruction of Spiking Activity from Calcium Imaging Data. J Neurophysiol doi: 10.1152/jn.00934.2017.
- Rahmati V, Kirmse K, Holthoff K, Schwabe L, Kiebel SJ (2017) Developmental Emergence of Sparse Coding: A Dynamic Systems Approach. Sci Rep 7:13015. DOI:10.1038/s41598-017-13468-z.
- Kirmse K, Hübner CA, Isbrandt D, Witte OW, Holthoff K (2017) GABAergic Transmission during Brain Development: Multiple Effects at Multiple Stages. The Neuroscientist. DOI: 10.1177/1073858417701382
- Kirmse K and Holthoff K (2017) Functions of GABAergic transmission in the immature brain. Neuroforum 23(1):A27–A33.
- Kummer M, Kirmse K, Zhang C, Haueisen J, Witte OW, Holthoff K (2016) Column-like Ca2+ clusters in the mouse neonatal neocortex revealed by three-dimensional two-photon Ca2+ imaging in vivo. Neuroimage 138, 64-75. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2016.05.050.
- Rahmati V, Kirmse K, Markovic D, Holthoff K, Kiebel SJ (2016) Inferring neuronal dynamics from calcium imaging data using biophysical models and Bayesian inference. PLoS Comput Biol 12(2): e1004736. doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004736
- Kummer M, Kirmse K, Witte OW, Haueisen J, Holthoff K (2015) A method to quantify accuracy of position feedback signals of a three-dimensional two-photon laser-scanning microscope. Biomed Opt Express 6(10):3678-3693.
- Kirmse K, Kummer M, Kovalchuk Y, Witte OW, Garaschuk O, Holthoff K (2015) GABA depolarizes immature neurons and inhibits network activity in the neonatal neocortex in vivo. Nat Commun 6:7750, doi:10.1038/ncomms8750
- Hübner CA and Holthoff K (2013). Anion transport and GABA signaling. Front Cell Neurosci 7:177. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2013.00177
- Kummer M, Kirmse K, Witte OW, Holthoff K (2012) Reliable in vivo identification of both GABAergic and glutamatergic neurons using Emx1-Cre driven fluorescent reporter expression, Cell Calcium 52: 182-189.
- Kirmse K, Witte OW, Holthoff K (2011) GABAergic depolarization during early cortical development and implications for anticonvulsive therapy in neonates, Epilepsia 52:1532-1543.
- Kirmse K, Witte OW, Holthoff K (2010) GABA depolarizes immature neocortical neurons in the presence of the ketone body ß-hydroxybutyrate, J Neurosci 30: 16002-16007.
- Holthoff K, Sagnak E, Witte OW (2007) Functional mapping of cortical areas with optical imaging, Neuroimage 37: 440-448.
- Stosiek C, Garaschuk O, Holthoff K, Konnerth A (2003) In vivo two-photon calcium imaging of neuronal networks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100: 7319-7324.
- Ludwig A, Budde T, Stieber J, Moosmang S, Wahl C, Holthoff K, Langebartels A, Wotjak C, Munsch T, Zong X, Feil S, Feil R, Lancel M, Chien KR, Konnerth A, Pape HC, Biel M, Hofmann F (2003) Absence epilepsy and sinus dysrhythmia in mice lacking the pacemaker channel HCN2. EMBO J 22: 216-224.
- Holthoff K, Witte OW (1998) Intrinsic optical signals in vitro: a tool to measure alterations in extracellular space with two-dimensional resolution. Brain Res Bull 47:649-655.
- Holthoff K, Witte OW (1997) Recording of neuronal network properties with near infrared dark field microscopy and microelectrodes. Electrochim Acta 42:3241-3246.
- Holthoff K, Witte OW (1996) Intrinsic optical signals in rat neocortical slices measured with near-infrared dark-field microscopy reveal changes in extracellular space. J Neurosci 16:2740-2749.
- Holthoff K, Dodt HU, Witte OW (1994) Changes in intrinsic optical signal of rat neocortical slices following afferent stimulation. Neurosci Lett 180:227-230.