ß-Catenin originally was identified as a component of the cadherin-catenin cell adhesion complex. Genetic experiments revealed a second function of ß-catenin within the Wnt signaling pathway. In unstimulated cells free ß-catenin is rapidly degraded by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway.
Binding of secreted Wnt proteins to Frizzled-LRP5/6 receptor complexes activates the canonical Wnt pathway. This results in the inhibition of the ß-catenin destruction complex and an intracellular accumulation of ß-catenin. Within the nucleus ß-catenin regulates transcription of target genes in binding to LEF/TCF transcription factors. Deregulated activation of this pathway by mutations of pathway components affects cell proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis. We are interested in the molecular mechanisms that modulate ß-catenin function. During recent years we identified new ß-catenin interaction partners using co-immunoprecipitation and pull-down assays with purified recombinant proteins and mapped the corresponding binding sites. To study the functional relevance of these new interaction partners, we use a broad spectrum of methods including reporter gene assays, real-time RT-PCR, ChIP and two-step ChIP, shRNA, cell proliferation, cell migration and anchorage independent growth experiments.
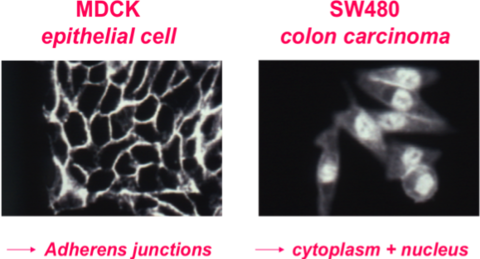
In MDCK cells ß-catenin is localized at adherens junctions in association with E-cadherin. In SW480 colon carcinoma cells, a mutation in the APC tumor suppressor protein, which is a component of the ß-catenin destruction complex, results in cytoplasmic and nuclear accumulation of ß-catenin.