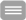Establishment of an automated platform for the transcriptome and epigenome analysis of single cells


In many diseases, epigenetic modifications through methylation of cytosines play an important role. Since changes in the epigenome of a cell affect the expression of genes, it would be desirable to correlate epigenetic changes directly with expression at the RNA level. In this project proposal a method for simultaneous high-throughput multi-parameter analysis of epigenome and transcriptome of individual cells will be developed and validated. The method will be used to characterize neurons and microglia in mouse models for selected neurodegenerative diseases at the single cell level. The next step is to check whether corresponding signatures can also be detected in blood cells of diseased animals. The method will also be used to characterize minimally invasive circulating tumor cells from patients with prostate cancer.
Schematic representation of the microfluidic system and the separation of indicated DNA and mRNA. A) Scheme of the principle of the "Drop-Seq" method (modified from Macosko et al., 2015, Cell). The particles, which are suspended in lysis reagent, are located in the central channel. The cells pass over the upper and lower channel and are trapped together with the particle in a droplet and lysed there. B) Heterogeneous tissue is dissociated into single cells and processed via the "Drop-Seq" method. After dissolution of the droplets, all indexed mRNA fragments can be amplified and sequenced. C, D) Set up of the mRNA primer (C) and DNA primer (D), consisting of a patient ID, the microparticle-individual specific barcode, the UMI (unique molecular identifier) and the mRNA adapter (poly-dT) or the DNA adapter sequence. E) Scheme of the preparation of microparticles to which cleavable DNA primer and non-cleavable mRNA primer are coupled which contain the same specific recognition sequence. After binding of the primer to mRNA or DNA, the mRNA on the microparticles can be separated magnetically from the DNA fragments and both can be independently sequenced. F) The required 2-fold primer synthesis is realized via an independently controlled deblocking and coupling of bases to the mRNA or DNA primer. G) Schematic of the Macosko et al. (2015) described "split and pool" method for generating specific recognition sequences that are coupled to microparticles. The assignment of the different mRNA species to a cell is carried out after sequencing by reading the randomly generated recognition sequence.